Verilen 2 string in anagram olup olmadigini kontrol edelim.
1. yontem:
Stringleri array e donusturelim. Sonra da sort edelim. Ve elemanlari esit mi diye kontrol edelim.
2. Yontem: Alfabe size inda bir array olusturalim. s1 icin a nin ascii den farkini ekleyelim. s2 icinse cikaralim. Son durumda eger anagramlarsa array in 0 olmasi beklenir.
ornegin a dan 2 b den 1 c ve d den 0 tane varsa
[2 1 0 0 ....] seklinde bir array olusur.
Aynilari s2 de varsa bunlari 0 a ceker.
Ascii karsiliklari : https://www.mediaclick.com.tr/blog/ascii-nedir
s1 = abba ve s2 = baba stringleri icin
s1 icin
a icin a(96) - a(96) = 0 oldugundan charArr[0] = 1 olur.
b icin b(97) - a(96) = 1 oldugundan charArr[1] = 1 olur.
b icin b(97) - a(96) = 1 oldugundan charArr[1] = 2 olur.
a icin a(96) - a(96) = 0 oldugundan charArr[0] = 2 olur.
Bu sekilde ilk string icin [2 2 0 0 0 0 0 .........] seklinde olur.
s2 icin
b icin b(97) - a(96) = 1 oldugundan charArr[1] = 2-1 = 1 olur.
a icin a(96) - a(96) = 0 oldugundan charArr[0] = 2 - 1 = 1 olur.
b icin b(97) - a(96) = 1 oldugundan charArr[1] = 1 - 1 = 0 olur.
a icin a(96) - a(96) = 0 oldugundan charArr[0] = 1 - 1 = 0 olur.
bu sekilde charArr de sadece [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...] seklinde oldugu icin sonuc bulunur.
FIRST UNIQUE CHARACTER
Verilen stringdeki ilk unique karakterin indexini dondurelim. Eger unique karakter yoksa -1 dondurelim.
Orn1: leetcode inputu icin ilk unique l dir. ve indexi 0 oldugu icin 0 output
Orn2 : loveleetcode inputu icin ilk unique v old icin indexi 2dir.
Bunun icin her harfi ve indexini iceren bir hashmap olusturalim. Eger ayni eleman mapte varsa o zaman valuesunu -1 olarak guncelleyelim
bu durumda leetcode icin
l 0
e -1
t 3
c 4
o 5
d 6
seklinde bir map olusur. Daha sonra bu map uzerinde donup valuesu -1 den buyuk en kucuk degeri bulana kadar doneriz.
FIRST SINGLE ELEMENT
Gelen inputta her eleman 2 defa olmasina ragmen tek kez var olan bir eleman vardir. onu bulunuz.
Orn:
[4, 2, 1, 2, 1] inputu icin
2 ve 1 sayilari 2 defa olmasina ragmen 4 sdece tek bir var. O yuzden sonuc 4 olacaktir.
Bunun icin hashset kullanabiliriz.
eger eleman sette yoksa ekleriz.varsa sileriz. bu sekilde 2 kez olan eleman eklenir ve silinir. Ama tek olan eleman sadece eklenir ve silinmeden kalir. Bu yuzden en sonda sette tek olan eleman vardir.
public static int singleElement(int arr[]) {
Set numSet = new HashSet();
for(int i : arr) {
if(numSet.contains(i)) {
numSet.remove(i);
}else {
numSet.add(i);
}
}
for(int j : numSet) {
return j;
}
return -1;
} MAX PROFIT
Input olarak verilen fiyatlarimiz olsun. Almadan once satamayiz. Amacimiz max kar elde etmek. Bunun icin alinmasi ve satilmasi gerekn gunleri output dondurmeliyiz.
int prices[] = new int[]{7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4};
System.out.println(maxProfit(prices));
2. gun alip 5. gun satmaliyiz
public static int maxProfit(int[] prices){
int sonuc = 0;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=0; i< prices.length; i++){
if(prices[i] < min){
min = prices[i];
}else{
sonuc = Integer.max(prices[i] - min, sonuc);
}
}
return sonuc;
}
COMMON ELEMENTS
Verilen 2 arraydaki common elamanlari dondurmek istensin. Bunun icin izleyecegimiz yontem asagidaki gibidir.
if(x=y=z ) x++ y++ z++
if(x<y) x++
if(y<z) y++
else z++
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int ar1[] = { 1, 5, 10, 20, 30};
int ar2[] = { 5, 13, 15, 20 };
int ar3[] = {5, 20};
System.out.print("Common elements are ");
findCommon(ar1, ar2, ar3);
}
public static void findCommon(int[] ar1, int[] ar2, int[] ar3) {
int x = 0, y = 0, z = 0;
int sonuc[] = new int[4];
while (x < ar1.length && y < ar2.length && z < ar3.length) {
if (ar1[x] == ar2[y] && ar1[x] == ar3[z]) {
System.out.print(" " + ar1[x]);
x++;
y++;
z++;
}
else {
if (ar1[x] < ar2[y]) {
x++;
}
else if (ar2[y] < ar3[z]) {
y++;
}
else {
z++;
}
}
}
}
}
FIND PEAK ELEMENT
1 2 3 1
Peak eleman etrafindaki elemanlardan buyuk olan elemandir. Bu input icin peak 3 tur. Cunku 2 ve 1 den buyuk. Ama bizim amacimiz 3u degil indexini yani 2 dondurmek.
1 2 1 3 5 6 4
inputu icin peak elemanlar 2 ve 6 dir. Bunlarin indexleri olan 1 veya 5 sonuc olarak kabul edilir.
Binary Search ile cozecegiz. O(logn)
Burda izlememiz gereken yontem (Liste sirali ise) once mid elemani bulmak. mid eleman sagindakinden kucukse peak eleman sagdadir diye sag tarafa gitmeliyiz. bunun icin baslangic mid+1, bitis ise degismez.
eger mid, mid-1 den buyukse o zaman peak eleman soldadir. bunun icin sola gitmeliyiz.
baslangic degismez ama bitis mid olur bu durumda.
public static int findPeak(int arr[]) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length -1;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if(arr[mid] < arr[mid+1]) {
left = mid+1;
}else {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}TWO SUM
Bir array ve bir target verilsin. Arraydaki hangi iki sayinin toplami bu target i verir bunu bulmak ve index leri dondurmek.
arr[] = 2, 7, 11, 15 ve target = 9 ise result = 0, 1 olmali cunku 2+7= 9 olur.
Izleyecegimiz yontem ise map olusturmak ve target-1 map te yoksa o andaki sayi ve indexini map e eklemek.
public static int[] twoSum(int arr[], int target) {
int result[] = new int[2];
Map map = new HashMap();
for(int i=0; i< arr.length; i++) {
if(!map.containsKey(target - arr[i])) {
map.put(arr[i], i);
}else {
result[0] = map.get(target-arr[i]);
result[1] = i;
break;
}
}
return result;
} BACKSPACE STRING COMPARE
Bu Google tarafindan sorulmus.
input1 : ab#c ve input2: ac#c olsun. # demek backspace yani sil demek. bu durumda input1: ac ve input2: ac olur. Esit olduklari true dondurmemiz gerekir.
public static boolean stringCompare(String s, String t) {
Stack<Character> sStack = new Stack<Character>();
Stack<Character> tStack = new Stack<Character>();
for(char sChar : S.toCharArray()) {
if(sStack.isEmpty() && sChar == '#') {
}
else if(sChar != '#') sStack.push(sChar);
else if (sChar == '#') sStack.pop();
}
for(char tChar : T.toCharArray()) {
if(tStack.isEmpty() && tChar == '#') {
}
else if(tChar != '#') tStack.push(tChar);
else if (tChar == '#') tStack.pop();
}
while(!sStack.isEmpty()) {
char currS = sStack.pop();
if(tStack.isEmpty() || tStack.pop() != currS) {
return false;
}
}
return sStack.isEmpty() && tStack.isEmpty();
} MOVE ZEROS
Sifirlari en sona tasiyacagiz.
[0 1 0 3 12] inputu icin output [1 3 12 0 0] olmalidir.
Yapacagimiz yontem soyle: 0 olmayan sayilar kac taneyse o indexten baslayarak 0lari yerlestircez.
bu ornekte 3 tane 0 olmayan sayi var o yuzden 3.index ten baslicaz 1 3 12 0 0 seklinde
bunun icin bir index tutcaz. 0 olmadikca onu arttircaz. Ve onceki 0 olan index e 0 olmayan sayiyi koycaz
public static int[] moveZeros(int arr[]) {
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] != 0) {
arr[index++] = arr[i];
}
}
for (int i = index; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = 0;
}
return arr;
}REVERSE INT
Verilen sayiyi tersine cevirme:
-123 icin -321, 120 icin 21, sayi Integer dan buyukse 0
public static int reverseInteger(int n) {
if(n>Integer.MAX_VALUE) return 0;
int sign = 1;
int rev = 0;
if(n < 0) {
sign = -1;
n *=-1;
}
while(n> 0) {
rev = (rev*10) + (n%10);
n = n/10;
}
return sign*rev;
}PLUS ONE
Bir array verilsin. Icindeki elemanlara bir sayiymis gibi davranip 1 arttirp sonucunu array olarak donelim.
[1,2,3] icin 123+1=124 old icin [1,2,4] donmeli.
[9,9] icin [1,0,0] donmeli.
Yontemimiz su sekilde olmali:
Sondan baslayarak o anki sayi 9dan kucukse bir arttiralim ve sonucu donelim.
Eger 9 sa o anki sayiyi 0 yapalim. Dongu devam etsin. Ornegin 99 icin [0,0] oldu. dongu bitti. Bu durumda yeni bir array olusturalim. Boyutu inputtan 1 buyuk olmali ve sadece ilk elemani 1 olmali. bu durumda [1,0,0] elde edilir.
public static int[] plusOne(int arr[]) {
for(int i=arr.length-1; i>=0;i--) {
if(arr[i] < 9) {
arr[i]++;
return arr;
}
arr[i] = 0;
}
int result[] = new int[arr.length +1];
result[0] =1;
return result;
} FIRST BAD VERSION
Bu soru facebook tarafindan sorulmus. Projedeki ilk bad version i bulmamizi istiyor. ornegin ilk bad version 4 ise bundan sonraki versiyonlarin hepsi bad dir.
bool isBadVersion(version) seklinde bir API verilmis olsun ve bu bad olup olmadigini donsun. Bizim yapmamiz gereken verilen n input u icin ilk bad version u bulmak.
ornegin: 0 good 1 bad version olsun, o halde versionlar 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 .... seklinde olur. Bu sekilde bir input icin bizim amacimiz ilk 1in indexini bulmaktir.
Bunun icinse Binary search kullanmamiz gerekir. O(logn)
public static int firstBadVersion(int n) {
int left = 0;
int right = n;
while(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left)/2;
if(!isBadVersion(mid)) {
left = mid+1;
}else {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}PAINT HOUSE
Evleri boyamak icin minimum costu bulmak gerekiyor. Yanyana olan evler ayni renk olamiyor.
cost[][] = [[17, 2, 17], [16, 16, 5], [14, 3, 19]] icin 2+ 5 + 3 = 10 dan minimum cost 10 olur. ilk katta min 2 sectigimiz icin 2. katta 1. indexteki 16yi secemeyiz. 0. index teki 16 ya da 5 den minimum olani secicez. 5 i sectik. 3. de ise 19 u secemeyiz. 14 ve 3 ten minimum olani secicez. 3 u sectik.
*** Array verilen inputlarda once error check yapmaliyiz.
public static int minCost(int[][] costs) {
if(costs == null || costs.length == 0) return 0;
for(int i=1; i < costs.length; i++) {
costs[i][0] += Math.min(costs[i-1][1], costs[i-1][2]);
costs[i][1] += Math.min(costs[i-1][0], costs[i-1][2]);
costs[i][2] += Math.min(costs[i-1][0], costs[i-1][1]);
}
return Math.min(Math.min(costs[costs.length-1][0],costs[costs.length-1][1]), costs[costs.length-1][2]);
}ROBOT RETURN TO ORIGIN
Bir robot dusunelim. 0,0 koordinatindan baslasin. Yaptigi hareketler sonucunda 0,0 noktasina donup donmedigini bulmaya calisalim. U: up, D: down, L:left, R: right anlamina gelsin.
Input: "UD" true doner. Cunku bir yukari bir asagi yine origine doner.
Input: "LL" false doner. Cunku 2 kez sola giderse 2 birim originden uzaklasmis olur.
Burda izleyecegimiz yontem su sekilde:
2 degisken tutalim. 1i yukari asagi icin. yukari giderse arttiralim, asagi inerse azaltalim.
2. degisken ise sag ve sol icin. Sola giderse arttiralim, saga giderse azaltalim.
Eger origine donerse bu degiskenlerin 0 olmasi gerekir.
public static boolean returnOrigin(String moves) {
int UD = 0;
int LR = 0;
for(int i=0; i< moves.length(); i++) {
switch (moves.charAt(i)) {
case 'U':
UD++;
break;
case 'D':
UD--;
break;
case 'L':
LR++;
break;
case 'R':
LR--;
break;
}
}
return UD == 0 && LR == 0;
}CONTAINS DUPLICATE II
Bir array icinde ayni sayi 2.defa varsa ilki ile aralarinda max k kadar index farki olmali. Buna uygun bir tane bile duplicate varsa true degilse false dondurcez.
orn1: [1, 2, 3, 1], k=3 icin 1 sayisi 0 ve 3 indexlerinde var. 3-0=3. 3<=k o yuzden true
orn2: [1, 0, 1, 1], k=1 icin 1 i 0 ve 2 olarak dusunursek 2-0<=k false old icin baska var mi bakalim.1 icin 2 ve 3. indexlere bakarsak 3-2<=k true. o yuzden true
orn3: [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3], k=2 icin 1 e bakalim. 3-0<=k degil. hic biri icin degil. o yuzden false.
Cozum yontemi.
Hashmap kullanalim. Sayi ve indeksini tutalim. Eger ayni sayi map te varsa aralarindaki farka bakalim. k den kucuk esitse true doneriz. Bi tane bile yeter. Degilse o andaki index i map e atmamiz lazim. map i guncelleriz.
Bu sekilde dongu bittiginde false doneriz.
public static boolean contains(int arr[], int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for(int i=0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(arr[i])) {
int prevIndex = map.get(arr[i]);
int diff = i - prevIndex;
if(diff <= k) {
return true;
}
map.put(arr[i], i);
}else {
map.put(arr[i], i);
}
}
return false;
}
FIND THE CELEBRITY
Bir partide celebrity olup olmadigini bulmaya calisiyoruz. Herkes onu taniyip o kimseyi celebritydir.
Eger celebrity yoksa -1 dondur. knows(a, b) adinda bir function default olarak tanimli olsun ve a , byi taniyor mu cevabini versin. Amacimiz knows() cagrimini azaltmak.
ilk basta bir tur donerek celebrity adayimizi bulmaya calisiyoruz. eger adayimiz i yi taniyorsa i celebrity olabilir. bunu kontrol etmek icin herkes i yi taniyor mu diye yeni bir dongu yapip kontrol etmeliyiz. eger i adayimiz degilse ve adayimiz birini taniyorsa veya hic biri adayimizi tanimiyorsa celebrity yoktur. -1 donduk.
public static int findCelebrity(int n) {
int candidate = 0;
for(int i=1; i < n; i++) {
if(knows(candidate, i)) {
candidate = i;
}
}
for(int i=0; i < n; i++) {
if(i != candidate && knows(candidate, i) || !knows(i, candidate)) {
return -1;
}
}
return candidate;
}INTERSECTION OF TWO ARRAYS
[1,2,2,1] ve [2,2] icin output: [2] olmali
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set set1 = new HashSet();
Set intersection = new HashSet();
for (int i : nums1) {
if (!set1.contains(i)) {
set1.add(i);
}
}
for(int i: nums2) {
if(set1.contains(i)) {
intersection.add(i);
}
}
int result[] = new int[intersection.size()];
int index = 0;
for(int i: intersection) {
result[index] = i;
index++;
}
return result;
} Cyclic Graph
bir array veriliyor ve kac adim rotate edilecegi soyleniyor. Arrayin son halini bulmamiz gerekiyor.
Orn: A = [3, 8, 9, 7, 6]
K = 3
icin output: [9, 7, 6, 3, 8]. 3 rotations were made:
[3, 8, 9, 7, 6] -> [6, 3, 8, 9, 7]
[6, 3, 8, 9, 7] -> [7, 6, 3, 8, 9]
[7, 6, 3, 8, 9] -> [9, 7, 6, 3, 8]
public int[] cyclicArray(int[] A, int K) {
int result[] = new int[A.length];
for(int i=0; i< A.length; i++) {
result[(i+K)%A.length] = A[i];
}
return result;
}Odd Number of Array
Arraydekii elemanlar hep 2 li sekilde verilmistir. 1 tanesinin ise pairi yoktur. Onu dondurelim.
Or: A arrayi icin
A[0] = 9 A[1] = 3 A[2] = 9
A[3] = 3 A[4] = 9 A[5] = 7
A[6] = 9
the elements at indexes 0 and 2 have value 9,
the elements at indexes 1 and 3 have value 3,
the elements at indexes 4 and 6 have value 9,
the element at index 5 has value 7 and is unpaired.
Amacimiz 7 yi dondurmek.
public static int oddNumberOfArray(int[] A) {
if(A == null || A.length == 0) return 0;
Set numSet = new HashSet();
for(int i:A) {
if(numSet.contains(i)) {
numSet.remove(i);
}else {
numSet.add(i);
}
}
for(int i: numSet) {
return i;
}
return 0;
}
Min Jump of Frog
bir kurbaga X konumunda ve her seferinde D kadar mesafe atlayarak Y veya Yden daha buyuk bir noktaya ulasmak
istiyor. Minimum atlama sayisini bulmamiz lazim.
Or: X = 10
Y = 85
D = 30
the function should return 3, because the frog will be positioned as follows:
after the first jump, at position 10 + 30 = 40
after the second jump, at position 10 + 30 + 30 = 70
after the third jump, at position 10 + 30 + 30 + 30 = 100
Missing One Element
N boyutlu bir arrayimiz var. Icindekii elemanlar 1 den baslayip N+1 e kadar gitmeli. Arrayde olmayan
elemani bulmamiz lazim.
Or: A[0] = 2
A[1] = 3
A[2] = 1
A[3] = 5
icin N=4. bu durumda 1,2,3,4,5 olmali arrayde. Olmayan eleman 4 oldugu icin output:4
Bunun formulu n(n+1)/2 olmali. Yani n=5 oluyor bu durumda.15 olmali toplami. ama su an toplam 11. o halde eksik olan 4tur.
Merge Two Sorted List
Elimizde 2 tane sorted list olsun ve biz bu iki listeyi sirali bir sekilde dondurelim. Ornegin
l1 = 1 -> 2 -> 4
l2 = 1 -> 3 -> 4
Sonucta ise 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 4 donmesini bekliyoruz.
Izleyecegimiz yontem su sekilde:
bos bir liste olusturalim, sonuclar icin bu listeyi kullanalim.
iki listenin ilk elemanlarini karsilastiralim. hangisi kucukse listeye ekleyelim. bu sekilde iki listede null olmadigi surece devam edelim. eger boyutlari esit degilse yani uzun olani listenin sonuna ekleyelim.
LinkedList Cycle
Elimize bir liste bir de pos adli parametre verilsin. pos anlami son node un kacinci index li elemana bagli oldugunu gostersin.
Ornegin :
VALID PALINDROME
Verilen ifadelerin palindrome olup olmadigini ogrenmek istiyoruz. Ama burda sadece harfleri ve sayilari kontrol edecegiz. Diger karakterleri, yani alfanumerik olmayan karakterleri, dikkate almayacagiz.
Ornegin :
A man, a plan, a canal: Panama
true dondurmeli. Bunun icin once alfanumerik olmayan olmayan karakterleri yeni bir string de birlestirelim. Daha sonra string lerde her zaman yaptigimiz gibi 2 tane pointer tanimlayalim. ilki en bastaki eleman, ikincisi son eleman. Ortaya kadar gelelim. Esitlerse true donmeli.
MIDDLE OF LINKEDLIST
Verilen bir linkedlist in middle elemani bulmaliyiz. Eger ortada iki eleman varsa ikinci elemani return etmeliyiz.
Linkedlist lerde kullanilan fast ve slow pointer yontemini kullanmaliyiz.
Burada fast pointer, slow un 2 kati hizla gider. fast sona ulasinca slow olan ortada olur, biz de slow u return edersek ortadaki elemani dondurmus oluruz.
KEYS AND ROOMS
Verilen arrayin anlami o index teki sayilara gidiliyor demek. Ornegin asagidaki input icin 0, index te 1 var. o yuzden 1. indexteki 2 ye gidiyoruz. burdan da 2. indexteki 3 e gidebiliyoruz. 3. indexteki odaya da gidebiliyoruz. Yani tum odalara gidebildigimiz icin true donuyoruz.
Not: 0 nolu oda kilitli degil. Yani 0 odaya her turlu gidilebiliyor.
input : [[1],[2],[3],[]]
output : true
Diger bir ornek ise
input : [[1,3],[3,0,1],[2],[0]]
output : false
Burda ise 2 nolu odaya hic gidilmiyor. O yuzden false donuyor.
burda oda sayisi boyutunda bir boolean array tutuyoruz. her bir odaya gidildikce o odayi true yapiyoruz. Bir tane de integer tipinde stack olusturup gidilen odalari ekliyoruz. Bunun sebebi ise daha sonra o stack te gezip gidilen odalardaki anahtarlari bulup gidilebilecek odalara da gidebilmek.
Container With Most Water
Verilen input array i icin olusturabilecek en buyuk array i bulmaya calisiyoruz. Ornegin
input : [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] icin
output : 49
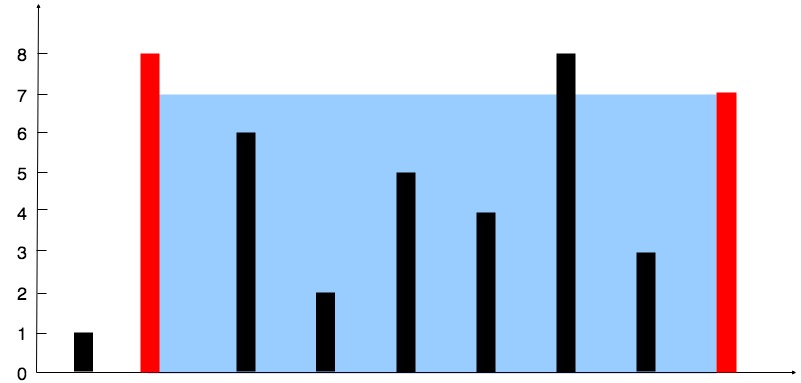
Gordugumuz gibi hem boy hem de en buyuk olmali. bunu kirmizi inputlari kullanarak 49 elde ettik.
Burda yapmamiz gereken 2 tane pointer kullanmak. Biri en basta. Digeri en sonda. Her ikili icin alani hesaplicaz ve buyukse max ile degistircez. Iki inputtan hangisi kucukse siradaki elemana gecicez. Ornegin ilk eleman 2.den kucukse en buyuk alani elde etmek icin ilkini diger eleman yapicaz. Buyuk olanla alanini bulucaz.
FIND DUPLICATE
Verilen bir arrayde mutlaka duplicate varsa bunu bulmak icin array i siralariz ve next i ile ayni olan eleman duplicate dir deriz.
input : [1,3,4,2,2]
output : 2
FIND ALL DUPLICATES IN LIST
Given an array of integers, 1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n (n = size of array), some elements appear twice and others appear once.
Find all the elements that appear twice in this array.
Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime?
Bu soru cok onemli mulakatlarda cikan bir soru. Dikkat edilmesi gereken detaylar elemanlarin 1 ile n arasinda olmasi. Ve ekstra space kullanmamamiz gerektigi.
Example:
Input:
[4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
Output:
[2,3]
1 ile n arasinda olmasindan yola cikarak su sekilde ilerleyelim. Her eleman index -1 e denk gelecek. ornegin 1 elemani 0. index te bulunacak. 2 elemani 1. index te bulunacak. Her bir eleman icin o elemanin -1 indexini negatif yapalim. Daha sonra ayni eleman tekrar geldiginde o index teki eleman negatif olacagindan daha once o elemani gorduk anlamina gelecek ve biz de o elemani duplicate listemize eklicez.
VALID PARANTHESIS STRING
bir kurbaga X konumunda ve her seferinde D kadar mesafe atlayarak Y veya Yden daha buyuk bir noktaya ulasmak
istiyor. Minimum atlama sayisini bulmamiz lazim.
Or: X = 10
Y = 85
D = 30
the function should return 3, because the frog will be positioned as follows:
after the first jump, at position 10 + 30 = 40
after the second jump, at position 10 + 30 + 30 = 70
after the third jump, at position 10 + 30 + 30 + 30 = 100
public int minJump(int X, int Y, int D) {
if((Y-X)%D == 0) {
return (Y-X)/D;
}return (Y-X)/D+1;
}Missing One Element
N boyutlu bir arrayimiz var. Icindekii elemanlar 1 den baslayip N+1 e kadar gitmeli. Arrayde olmayan
elemani bulmamiz lazim.
Or: A[0] = 2
A[1] = 3
A[2] = 1
A[3] = 5
icin N=4. bu durumda 1,2,3,4,5 olmali arrayde. Olmayan eleman 4 oldugu icin output:4
Bunun formulu n(n+1)/2 olmali. Yani n=5 oluyor bu durumda.15 olmali toplami. ama su an toplam 11. o halde eksik olan 4tur.
public static int missingOneElement(int[] A) {
long N = data.length + 1;
long total = (N * (N + 1)) / 2;
long sum = 0L;
for (int i : data) {
sum += i;
}
return (int)(total - sum);
}Merge Two Sorted List
Elimizde 2 tane sorted list olsun ve biz bu iki listeyi sirali bir sekilde dondurelim. Ornegin
l1 = 1 -> 2 -> 4
l2 = 1 -> 3 -> 4
Sonucta ise 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 4 donmesini bekliyoruz.
Izleyecegimiz yontem su sekilde:
bos bir liste olusturalim, sonuclar icin bu listeyi kullanalim.
iki listenin ilk elemanlarini karsilastiralim. hangisi kucukse listeye ekleyelim. bu sekilde iki listede null olmadigi surece devam edelim. eger boyutlari esit degilse yani uzun olani listenin sonuna ekleyelim.
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x){
val = x;
}
}
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode resultList = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode head = resultList;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if(l1.val < l2.val) {
resultList.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else {
resultList.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
resultList = resultList.next;
}
if(l1 != null) {
resultList.next = l1;
}else {
resultList.next = l2;
}
return head;
}
LinkedList Cycle
Elimize bir liste bir de pos adli parametre verilsin. pos anlami son node un kacinci index li elemana bagli oldugunu gostersin.
Ornegin :
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.Example 2:Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0 Output: true Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.Example 3:Input: head = [1], pos = -1 Output: false Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.Cozum:Linkedlist lerde kullanilan yontem fast ve slow node yontemidir. Burada da onu kullanacagiz. Slow node listede tek tek ilerlerken fast node cifter ilerler.or:slow = head;fast = head.next;sonra :slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;seklinde ilerler. Bu yontemle eger fast in next i null degilse listemizde cycle var demektir.class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; next = null; } } public class CycleList { public static boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) { if(head == null) return false; ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head.next; while(slow != fast) { if(fast == null || fast.next == null) { return false; } slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } return true; } }REVERSE STRING
Verilen bir arrayi tersine cevirip dondurmeliyiz. Ama bunu inplace arrayde yapmaliyiz.Ornegin :
input : ['H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
output: ['o', 'l', 'l', 'e', 'H']
olmali.Bunun icin pointer kullanmaliyiz. Biri arrayin basinda biri sonunda.Ve bunlari swap etmeliyiz. Ortaya kadar getirmeliyiz.
public static void reverseString(char[] s) {
int first_pointer = 0;
int second_pointer = s.length - 1;
while(first_pointer < second_pointer){
char temp = s[second_pointer];
s[second_pointer] = s[first_pointer];
s[first_pointer] = temp;
first_pointer ++;
second_pointer--;
}
}
VALID PALINDROME
Verilen ifadelerin palindrome olup olmadigini ogrenmek istiyoruz. Ama burda sadece harfleri ve sayilari kontrol edecegiz. Diger karakterleri, yani alfanumerik olmayan karakterleri, dikkate almayacagiz.
Ornegin :
A man, a plan, a canal: Panama
true dondurmeli. Bunun icin once alfanumerik olmayan olmayan karakterleri yeni bir string de birlestirelim. Daha sonra string lerde her zaman yaptigimiz gibi 2 tane pointer tanimlayalim. ilki en bastaki eleman, ikincisi son eleman. Ortaya kadar gelelim. Esitlerse true donmeli.
public static boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
String fixed_string = "";
for(char c : s.toCharArray()){
if(Character.isDigit(c) || Character.isLetter(c)) {
fixed_string += c;
}
}
fixed_string = fixed_string.toLowerCase();
int first_pointer = 0;
int second_pointer = fixed_string.length() -1;
while(first_pointer < second_pointer) {
if(fixed_string.charAt(first_pointer) != fixed_string.charAt(second_pointer)) {
return false;
}
first_pointer ++;
second_pointer --;
}
return true;
}
MIDDLE OF LINKEDLIST
Verilen bir linkedlist in middle elemani bulmaliyiz. Eger ortada iki eleman varsa ikinci elemani return etmeliyiz.
Linkedlist lerde kullanilan fast ve slow pointer yontemini kullanmaliyiz.
Burada fast pointer, slow un 2 kati hizla gider. fast sona ulasinca slow olan ortada olur, biz de slow u return edersek ortadaki elemani dondurmus oluruz.
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}KEYS AND ROOMS
Verilen arrayin anlami o index teki sayilara gidiliyor demek. Ornegin asagidaki input icin 0, index te 1 var. o yuzden 1. indexteki 2 ye gidiyoruz. burdan da 2. indexteki 3 e gidebiliyoruz. 3. indexteki odaya da gidebiliyoruz. Yani tum odalara gidebildigimiz icin true donuyoruz.
Not: 0 nolu oda kilitli degil. Yani 0 odaya her turlu gidilebiliyor.
input : [[1],[2],[3],[]]
output : true
Diger bir ornek ise
input : [[1,3],[3,0,1],[2],[0]]
output : false
Burda ise 2 nolu odaya hic gidilmiyor. O yuzden false donuyor.
burda oda sayisi boyutunda bir boolean array tutuyoruz. her bir odaya gidildikce o odayi true yapiyoruz. Bir tane de integer tipinde stack olusturup gidilen odalari ekliyoruz. Bunun sebebi ise daha sonra o stack te gezip gidilen odalardaki anahtarlari bulup gidilebilecek odalara da gidebilmek.
public boolean canVisitAllRooms(List> rooms) {
boolean[] seen = new boolean[rooms.size()];
seen[0] = true;
Stack visited = new Stack();
visited.push(0);
while(!visited.isEmpty()) {
int curr_index = visited.pop();
for(int elem : rooms.get(curr_index)) {
if(!seen[elem]){
seen[elem] = true;
visited.push(elem);
}
}
}
for(boolean index : seen) {
if(!index) return false;
}
return true;
}
Container With Most Water
Verilen input array i icin olusturabilecek en buyuk array i bulmaya calisiyoruz. Ornegin
input : [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] icin
output : 49

Gordugumuz gibi hem boy hem de en buyuk olmali. bunu kirmizi inputlari kullanarak 49 elde ettik.
Burda yapmamiz gereken 2 tane pointer kullanmak. Biri en basta. Digeri en sonda. Her ikili icin alani hesaplicaz ve buyukse max ile degistircez. Iki inputtan hangisi kucukse siradaki elemana gecicez. Ornegin ilk eleman 2.den kucukse en buyuk alani elde etmek icin ilkini diger eleman yapicaz. Buyuk olanla alanini bulucaz.
public static int maxArea(int[] height) {
int first_pointer = 0;
int last_pointer = height.length -1;
int area = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int counter = 0;
while(first_pointer < last_pointer) {
if(height[first_pointer] < height[last_pointer]) {
area = Math.max(area, height[first_pointer] * (last_pointer - first_pointer));
first_pointer ++;
}else {
area = Math.max(area, height[last_pointer] * (last_pointer - first_pointer));
last_pointer --;
}
}
return area;
}FIND DUPLICATE
Verilen bir arrayde mutlaka duplicate varsa bunu bulmak icin array i siralariz ve next i ile ayni olan eleman duplicate dir deriz.
input : [1,3,4,2,2]
output : 2
public static int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i=0; i< nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] == nums[i+1]) {
return nums[i];
}
}
return -1;
}FIND ALL DUPLICATES IN LIST
Given an array of integers, 1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n (n = size of array), some elements appear twice and others appear once.
Find all the elements that appear twice in this array.
Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime?
Bu soru cok onemli mulakatlarda cikan bir soru. Dikkat edilmesi gereken detaylar elemanlarin 1 ile n arasinda olmasi. Ve ekstra space kullanmamamiz gerektigi.
Example:
Input:
[4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
Output:
[2,3]
1 ile n arasinda olmasindan yola cikarak su sekilde ilerleyelim. Her eleman index -1 e denk gelecek. ornegin 1 elemani 0. index te bulunacak. 2 elemani 1. index te bulunacak. Her bir eleman icin o elemanin -1 indexini negatif yapalim. Daha sonra ayni eleman tekrar geldiginde o index teki eleman negatif olacagindan daha once o elemani gorduk anlamina gelecek ve biz de o elemani duplicate listemize eklicez.
public static List findDuplicates(int[] nums) {
List duplicates = new ArrayList();
for(int i=0; i< nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[makePositive(nums[i]) -1] < 0) {
duplicates.add(makePositive(nums[i]));
}else {
nums[makePositive(nums[i]) -1] = nums[makePositive(nums[i]) -1] *-1;
}
}
return duplicates;
}
public static int makePositive(int i) {
if(i < 0) return i*-1;
return i;
} VALID PARANTHESIS STRING
Acilan sayida ve sirada kapali parantez icermeli. Birkac ornek yazalim:
{}() true
({()}) true
{}( false
[] true
public static boolean validParanthesisString(String str) {
if(str.length() % 2 != 0) return false;
Stack stack = new Stack();
for(int i=0; i< str.length(); i++) {
if(str.charAt(i) == '{' || str.charAt(i) == '(' || str.charAt(i) == '[') {
stack.push(str.charAt(i));
}else {
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}else if(str.charAt(i) == '}' && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '{') {
stack.pop();
}else if(str.charAt(i) == ')' && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '(') {
stack.pop();
}else if(str.charAt(i) == ']' && !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == '[') {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
} VALID PARANTHESIS STRING WITH HASHMAP
public static boolean validParanthesisStringWithMap(String str) {
if(str.length() % 2 != 0) return false;
Stack stack = new Stack();
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put('}', '{');
map.put(']', '[');
map.put(')', '(');
for(int i=0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(!map.containsKey(str.charAt(i))) {
stack.push(str.charAt(i));
}else {
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
if(stack.pop() != map.get(str.charAt(i))) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
Bu kisaca bir fibonacci serisidir.
public static int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n <= 0) return 0;
if(n == 1) return 1;
if(n == 2) return 2;
int one_step_before = 2;
int two_steps_before = 1;
int all_ways = 0;
for(int i=2; i < n; i++){
all_ways = one_step_before + two_steps_before;
two_steps_before = one_step_before;
one_step_before = all_ways;
}
return all_ways;
}CYCLIC ROTATION
N integerdan olusan bir array ve K integer inputu verilcek. Ve bu array'i sagdan K defa dondurecegiz. Son durumdaki array i return edecegiz.
For example, given
A = [3, 8, 9, 7, 6]
K = 3
the function should return [9, 7, 6, 3, 8]. Three rotations were made:
[3, 8, 9, 7, 6] -> [6, 3, 8, 9, 7]
[6, 3, 8, 9, 7] -> [7, 6, 3, 8, 9]
[7, 6, 3, 8, 9] -> [9, 7, 6, 3, 8]
Write a function:
class Solution { public int[] solution(int[] A, int K); }
public int[] solution(int[] A, int K){
int rotatedA[] = new int[A.length];
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i++){
index = (i+K) % A.length;
rotatedA[index] = A[i];
}
return rotatedA;
}BINARY GAP
Verilen inputun binary representation'ini bulunur. 1 ler arasinda en uzun mesafe return edilir.
Ornegin : number 9 has binary representation 1001 and contains a binary gap of length 2. The number 529 has binary representation 1000010001 and contains two binary gaps: one of length 4 and one of length 3. The number 20 has binary representation 10100 and contains one binary gap of length 1. The number 15 has binary representation 1111 and has no binary gaps.
public static int solution(int N) {
int currentBit = 0, currentGap = 0, maxGap =0;
if(N!=1 || N!=0){
while(N != 0) {
currentBit = N%2;
N = N/2;
if(currentBit == 1) {
if(currentGap > maxGap) {
maxGap = currentGap;
}
currentGap = 0;
}else {
currentGap++;
}
}
}
return maxGap;
}Bir sayinin binary'sini bulmak icin : sayiyi surekli 2ye bol. Taa ki 0 olana kadar. 2ye bole ve kalani sondaki basamaktan baslayarak yaz.
Ornegin : 4 icin
4/2 = 2 , kalan : 0 -> 0
2/2 = 1, kalan : 0 -> 00
1/2 = 0, kalan: 1 -> 100
seklinde.
MINIMUM POSITIVE INTEGER NOT IN ARRAY
Bir array veriliyor ve bu arrayda olmayan en kucuk positif sayiyi return etmemiz gerekiyor.
Orn:
A = [1,2,3] icin 4 return etmeli.
B = [1,3,6,4,1,2] icin 5 return etmeli.
Burada len+1 olacak sekilde bir boolean array olusturalim. Ve o ankii deger 0 dan buyuk oldugu surece ve length den kucuk oldugu surece o degerin karsiligini true setleyelim.
public static int solution2(int[] A) {
boolean present[] = new boolean[A.length +1];
for(int i=0; i< A.length; i++) {
if(A[i]> 0 && A[i] <= A.length) {
present[A[i]] = true;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i<= A.length; i++) {
if(!present[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return A.length +1;
}


Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder